MICROFERTILIZATION & ICSI
What is Conventional Egg Microsurgery (ICSI)?
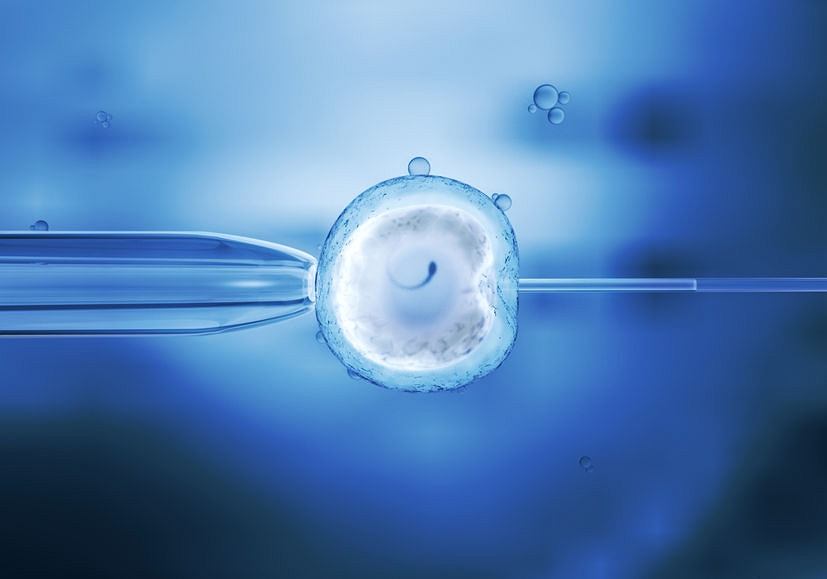
The micro-insemination (ICSI) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection, is the procedure in IVF in which a single spermatozoon is inserted directly into the egg in order to fertilize it.
The embryologist selects a morphologically standard spermatozoon and places it inside the egg’s cytoplasm with the help of the micro-insemination technique so that the insertion can be achieved more easily.
Read more details about the role of the embryologist here.
This method has become very popular due to its high effectiveness and success rates.
When is it used?
In which cases do we select it as treatment
1. Male Infertility
Micro-insemination is selected as treatment:
– In cases of severe Oligoasthenospermia or Asthenospermia. More specifically, when the sperm has less than 5.000.000 mobile spermatozoa after being processed, or when the sperm has low motility and anti-sperm antibodies.
– If there is a history of obstructive and non-obstructive azoospermia.
– If the spermatozoa have no acrosome (section of the head) which is a special enzyme that allows them to penetrate the egg’s walls and achieve pregnancy (globozoospermia).
– In cases where the spermatozoa exhibit extensive agglutination. This immunological cause of infertility appears when the spermatozoa connect with each other and inevitably greatly reduce their motility.
– If there are ejaculation issues
– When using frozen sperm in cases of patients that have undergone cancer treatment (chemotherapy or radiotherapy)
Read more on the causes of infertility in this article.
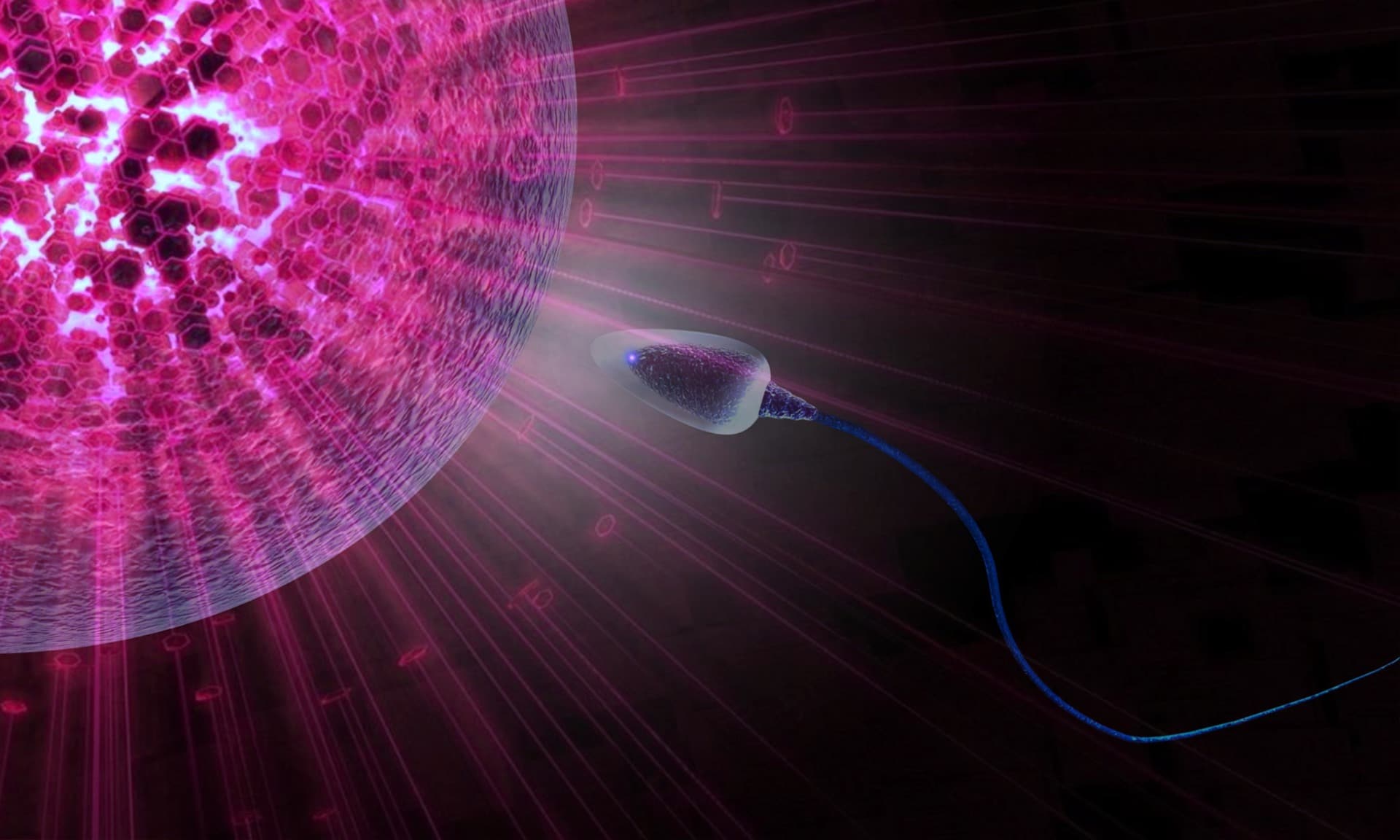

2. Eggs
When the eggs have a transparent shell that is thicker and tougher than usual, inevitably impeding or preventing the spermatozoa from penetrating the egg’s wall.
3. Failed Past Attempts

How is the ICSI Method carried out?
Detailed, Step by step procedure
According to the treatment protocol of the typical IVF procedure, the first step is to stimulate the woman’s ovaries so that the egg retrieval can take place. Then the eggs are subjected to a special enzyme treatment in order to separate them from the surrounding grainy cells and make them much easier to handle. This stage takes about 1 – 2 minutes. The most mature and suitable eggs are selected for the ICSI procedure.
During the same day, the partner’s sperm sample is also collected and processed depending on the quantity and the motility of the spermatozoa. If the sperm sample is insufficient, the partner is called to donate some more later that day. Even a few dozens of mobile spermatozoa in the sample are enough for the ICSI procedure to go ahead as normal.
In the next step, one-by-one the eggs are immobilized with the help of a thin, glass pipette. Another even thinner glass pipette (which greatly resembles an injection needle) is used to isolate each spermatozoon so that it can enter the cytoplasm of each egg. Each attempt to merge sperm and egg only takes a few seconds but the whole procedure can last for hours depending on the amount of spermatozoa and how easy they are to find.
The following step sees the eggs being placed in special cultivation equipment until they are fertilized and so produce new embryos.
After the blastocyst creation, the new embryos are evaluated and the best ones are selected for Embryo Transfer.
In Greece, the success rate of the Micro-insemination technique is about 65% – 75%, with the age of the patient playing a vital role in the outcome.
The embryologist’s experience and expertise constitute the most important factor of success in an ICSI attempt.
Read this very useful article about the success rates of In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) and Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
The positive outcome of the ICSI method depends on:
– the sustainability of the spermatozoon
– the egg quality
– the eggs’ successful activation
– the eggs’ ability to endure the endocytoplasmic procedure
– the woman’s age